-
1. The cutting edge needs to be how many more times harder than the workpiece material?
A3 times harder than the workpiece. B1 time harder than the workpiece. CDoes not really matter. -
2. When machining is carried out what happens at the cutting edge?
AThe cutting edge is subjected to impact and some heat. BThe cutting edge is subjected to severe impact and extremely high temperatures. CThe cutting edge should be 3 times harder than that of the workpiece material. -
3. A carbon steels basic components consists of?
AIron (Fe) and carbon (C). BIron (Fe), carbon (C) and nickel (Ni). CIron (Fe), nickel (Ni), and chromium (Cr). -
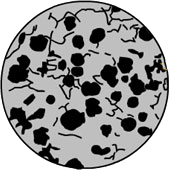
4. The image shows which type of cast iron?
AGrey cast iron. BDuctile cast iron. -
5. Workpiece materials are classified according to the ISO standards. Which of the following is correct?
AAll workpiece materials P, M, K, N, S, H are classified by the type of chip generated. BWorkpiece materials in the P, M, K groups are determined by the way in which the chips generate. CNone of the groups are classified according to the type of chips that are generated. -
6. For the Rockwell hardness test how many are introduced in this course?
A3 Rockwell scales. B5 Rockwell scales. C4 Rockwell scales. -
7. As the hardness of a workpiece increases what can happen;
AThe amount of welding can increase. BThe amount of flank wear can increase. CThe chips become more difficult to break. -
8. One method of reducing the cutting resistance when turning is to;
AIncrease the rake angle. BDecrease the rake angle. CDecrease the cutting speed. -
9. If the thermal conductivity of a workpiece material is low then the heat does not diffuse into the chip or surrounding work, but locates at the cutting edge. This can result in;
ASoftening of the cutting edge leading to plastic deformation. BAn increase in cutting resistance leading to reduced wear. CAn increase in cutting resistance and higher surface finishes. -
10. If a workpiece material has high affinity, when the cutting edge is subject to high cutting edge temperatures, the cutting edge and the workpiece react. This will result in;
AAdhesion and large rake wear. BSoftening of the cutting edge and high rake wear. CIncrease in chip control and high flank wear. -
- Next
- Try again
Result