![]() For steels
For steels
![]() For stainless steels
For stainless steels
![]() For cast iron
For cast iron
![]() For non-ferrous metal
For non-ferrous metal
![]() For difficult to cut material
For difficult to cut material
![]() For hardened material
For hardened material
We are surrounded by many metallic goods in our everyday life. Do you know how these products are manufactured?
There are many ways to machine metals, but the most commonly used method is cutting. Here we are going to learn about cutting tools and cutting processes. What do we mean by saying cutting tools?
First, let's look at some examples of cutting tools that are in our daily life. Knives and graters in the kitchen, scissors and pencil sharpeners on the desk, and a saw and plane in the storeroom are all cutting tools.
These cutting tools share a common property which is that they all change shapes of things by cutting and producing chips.
As you know by now, cutting tools are tools that cut things to acquire a desired shape. Cutting tools in our daily life cut fruits, vegetables, and wood, but the cutting tools produced by Mitsubishi Materials cut harder materials such as steel.
Now, let's look at cutting tools which machine steel, the main material in the industrial world.

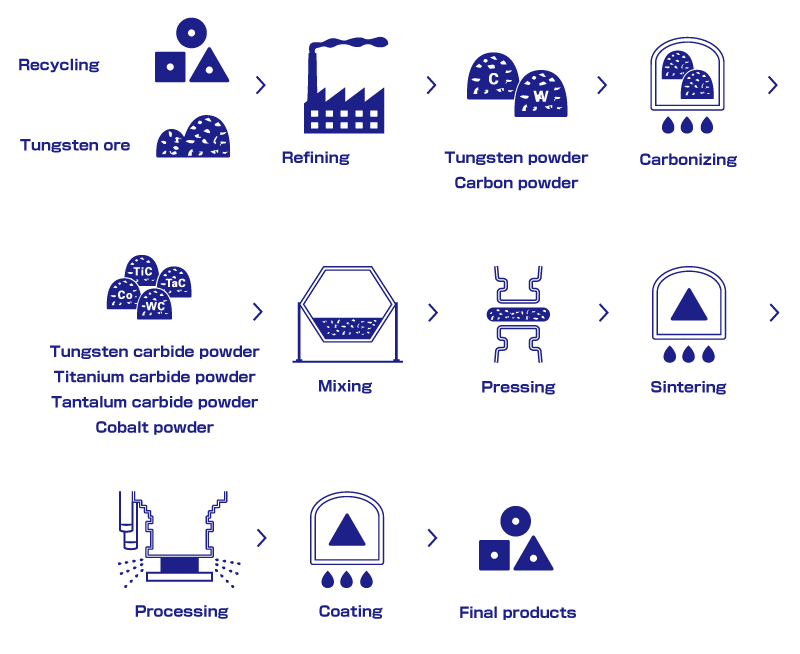
Let's see the manufacturing process of carbide.
First, mix tungsten carbide with cobalt to make powder which can be classified as raw materials. The granulated mixture is poured into a die cavity and pressed. It gives a moderate strength like that of chalk.
Next, the pressed compacts are placed in a sintering furnace and heated at a temperature of about 1400°C, resulting in cemented carbide.
After sintering, content volume shrinks considerably.
Also, hardness of cemented carbide is at a level between diamond and sapphire and weight is about twice as iron.
Then, how do we cut this hard cemented carbide?
The figure on the right shows the condition of a cutting edge during machining. The cutting edge cuts the workpiece and chips are produced. The temperature at the top of the cutting edge becomes as high as 800°C because of impact and friction.
Cemented carbide grades that can withstand these high temperatures are the most successful.
Carbide formed into different configurations are the most popular, and they are called indexable inserts. Indexable inserts are used for various shapes of holders and selected according to shape of the workpiece and cutting mode.


External holder and internal boring bar produce round shaped workpieces. Machining processes that use holders or boring bars is called turning, and its main characteristic is that workpieces rotate.
The machine used for turning is called a lathe.
The tool in the photo on the right is a milling tool. Milling tools can be divided into two types ; one is face milling which machines the workpiece surface and the other is endmilling which performs slotting shoulder milling etc.. Machining modes that use facemills and endmills are called milling operations, and its main characteristic is that the tools rotate. The machine used for milling is called a milling machine.

The photo on the right is a tool that produces circular holes in workpieces and is called a drill. Indexable insert type drills and brazed drills produce relatively large holes and solid drills produce smaller holes. The main characteristic of drilling is that it can be used for both milling and turning machines.

As mentioned above, cutting mode is composed of three main styles ; turning, milling, and drilling. By choosing an appropriate cutting tool according to the cutting mode, hard metals can be machined efficiently.
Today cemented carbide tools have become a primary means for increasing metal cutting productivity, while research constantly develops new products for more accurate and faster machining to reduce manufacturing costs.
Technical consultation from here
24/7Contact form Japan
Japan Japan
Japan United States
United States Mexico
Mexico Brazil
Brazil EU
EU United Kingdom
United Kingdom Germany
Germany Spain
Spain France
France Italy
Italy Poland
Poland Turkey
Turkey Czechia
Czechia China
China South East Asia, Oceania, South Africa
South East Asia, Oceania, South Africa India
IndiaNecessary cookies are used to help this website function properly.
For example, they provide login retention functionality.
Analytical cookies collect information about your use of this website in an anonymous and aggregated form. These cookies are used to analyze and improve the functionality of this website.
These cookies enable this website to provide enhanced functionality and personalisation. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Functional cookies are used by social networking services to track the use of their built-in features. For example, these cookies allow you to share pages from this website with your social network.
Advertising cookies may be set through this website by our advertising partners based on the data obtained. They identify your unique browser and Internet device and may be used to provide anonymized demographic data, build profiles of your interests, and display advertising relevant to those interests.
![]() For steels
For steels
![]() For stainless steels
For stainless steels
![]() For cast iron
For cast iron
![]() For non-ferrous metal
For non-ferrous metal
![]() For difficult to cut material
For difficult to cut material
![]() For hardened material
For hardened material
![]() For finish cutting
For finish cutting
![]() For medium cutting
For medium cutting
![]() For rough cutting
For rough cutting